Blockchain security audits are critical evaluations that identify and mitigate vulnerabilities within blockchain systems, ensuring the secure operation and integrity of the network.

In the dynamic world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, the security of digital assets and transactions is a critical concern. As blockchain technology continues to disrupt traditional financial systems with its decentralized approach, ensuring the integrity and safety of this innovative space is paramount. Blockchain security audits have emerged as a vital tool in safeguarding blockchain ecosystems against a myriad of security threats.
The Essence of Blockchain Security
Blockchain’s security prowess is largely attributed to its decentralized nature and the use of cryptographic hashing. Each transaction is chronologically recorded in blocks, which are cryptographically linked to form an immutable chain. Despite this robust structure, blockchains are not impervious to security breaches.
Vulnerabilities in the Blockchain Space
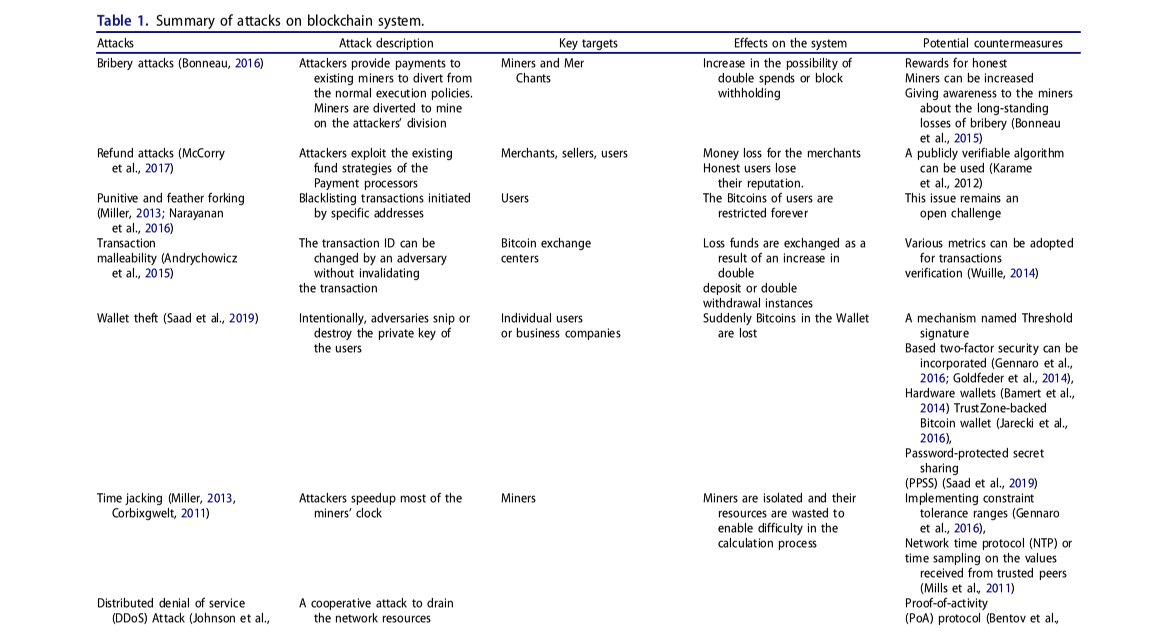
Several security threats loom over blockchain networks, including:
– Smart Contract Flaws: Smart contracts are prone to bugs that can be exploited, leading to incidents like reentrancy attacks and overflow/underflow errors.
– 51% Attacks: Dominating over half of a network’s mining power can enable attackers to manipulate transactions and double-spend.
– Private Key Security: The loss or theft of private keys can grant attackers unauthorized access to blockchain assets.
– Forks and Consensus Disputes: Disagreements over blockchain forks can threaten the network’s stability and security.
– Malicious Nodes: Nodes with nefarious intentions can perform sybil or eclipse attacks, undermining the network’s defenses.
– Oracle Manipulation: Reliance on external data feeds, or oracles, introduces a risk if these sources are compromised.
Conducting a Blockchain Security Audit
A blockchain security audit is a meticulous process that scrutinizes every aspect of a blockchain’s security framework to pinpoint weaknesses and potential attack vectors. It is a critical step in reinforcing the trustworthiness of blockchain platforms.
Key Focus Areas of a Blockchain Security Audit
– Code Review: Auditors meticulously examine the blockchain’s codebase, particularly smart contracts, for any security gaps or inefficiencies.
– Network Analysis: The network’s design is evaluated to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
– Consensus Mechanism Scrutiny: The underlying consensus algorithm is assessed for potential weaknesses that could be targeted.
– Private Key Management: The processes surrounding the generation, storage, and management of private keys are audited for security flaws.
– Smart Contract Evaluation: A deep dive into smart contracts checks for vulnerabilities, gas usage optimization, and execution accuracy.
– Third-party Service Assessment: The security and reliability of integrated third-party services, such as oracles and APIs, are thoroughly vetted.
Steps to Perform a Blockchain Security Audit
– Define Audit Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of the audit to maintain focus and direction throughout the process.
– Identify Components and Data Flows: Understand the architecture, components, and data flows within the target system to ensure a comprehensive audit.
– Assess Potential Security Risks: Evaluate the blockchain’s nodes, APIs, and communication protocols for any security risks that may arise.
– Threat Modeling: Employ threat modeling techniques to identify and understand potential security issues within the system.
– Exploitation and Remediation: Test the identified vulnerabilities to gauge their severity and develop strategies to remediate them.
Blockchain security audits are indispensable in the quest to maintain a secure and trustworthy blockchain environment. As digital assets and decentralized applications gain prominence, the need for rigorous security measures becomes increasingly evident. By adhering to the guidelines detailed in this guide, blockchain practitioners can proactively detect and rectify security vulnerabilities, fostering a more secure blockchain ecosystem for all users. It is crucial to remember that blockchain security is not a one-time event but a continuous process that should be integrated into the lifecycle of any blockchain project. Regular audits are essential to adapt to the evolving threat landscape and uphold the security standards necessary for the flourishing of blockchain technology.